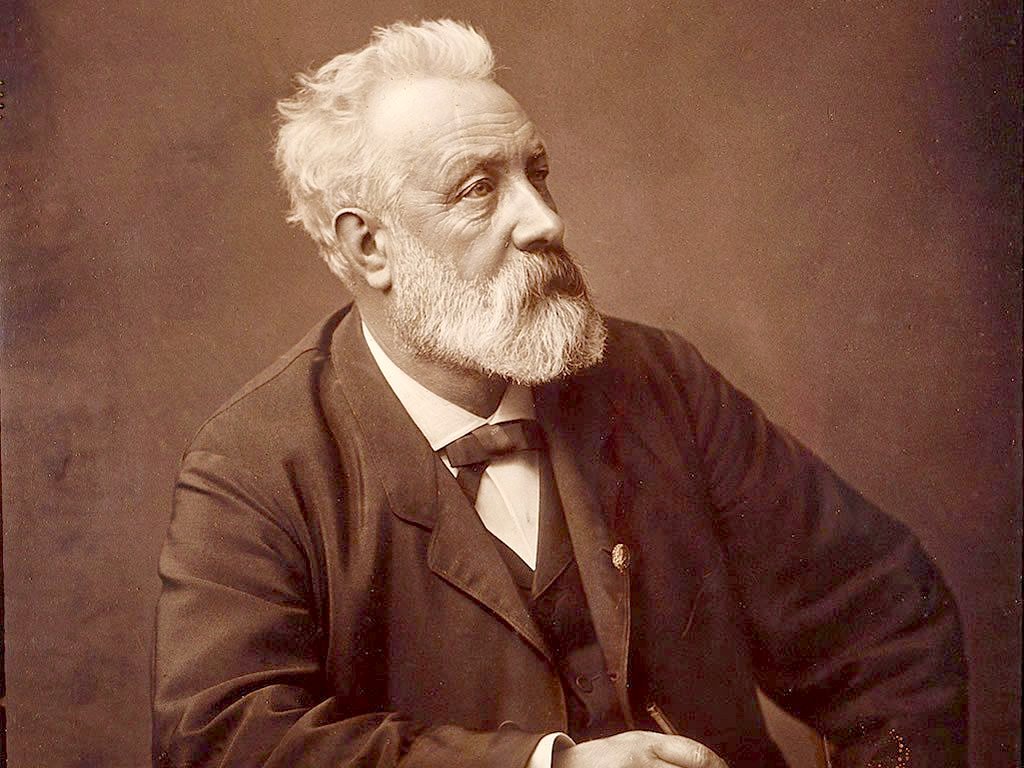|
What
a wonderful imagination the French writer had. He was also a practical
mariner, gaining much of his material from his travels, just like Herman
Melville, for his Moby
Dick. Jules Verne is best known for '20,000
Leagues Under the Sea' and Around
The World In Eighty Days. But he also authored a number of other
popular novels, that made it onto the big screen, such as 'The
Mysterious Island,' and 'Journey To The Centre Of The World.'
PUBLISHER
In 1862, through their mutual acquaintance Alfred de Bréhat,
Jules Verne came into contact with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel, and submitted to him the manuscript of his developing novel, then called Voyage en
Ballon.
Hetzel, already the publisher of Honoré de Balzac, George Sand, Victor Hugo, and other well-known authors, had long been planning to launch a high-quality family magazine in which entertaining fiction would combine with scientific education. He saw Verne, with his demonstrated inclination toward scrupulously researched adventure stories, as an ideal contributor for such a magazine, and accepted the novel, giving Verne suggestions for improvement. Verne made the proposed revisions within two weeks and returned to Hetzel with the final draft, now titled Five Weeks in a Balloon. It was published by Hetzel on 31 January 1863.
To secure his services for the planned magazine, to be called the Magasin d'Éducation et de Récréation (Magazine of Education and Recreation), Hetzel also drew up a long-term contract in which Verne would give him three volumes of text per year, each of which Hetzel would buy outright for a flat fee. Verne, finding both a steady salary and a sure outlet for writing at last, accepted immediately. For the rest of his lifetime, most of his novels would be serialized in Hetzel's Magasin before their appearance in book form, beginning with his second novel for Hetzel, The Adventures of Captain Hatteras (1864–65).
When The Adventures of Captain Hatteras was published in book form in 1866, Hetzel publicly announced his literary and educational ambitions for Verne's novels by saying in a preface that Verne's works would form a novel sequence called the Voyages extraordinaires (Extraordinary Voyages or Extraordinary Journeys), and that Verne's aim was "to outline all the geographical, geological, physical, and astronomical knowledge amassed by modern science and to recount, in an entertaining and picturesque format that is his own, the history of the universe". Late in life, Verne confirmed that this commission had become the running theme of his novels: "My object has been to depict the earth, and not the earth alone, but the universe… And I have tried at the same time to realize a very high ideal of beauty of style. It is said that there can't be any style in a novel of adventure, but it isn't true." However, he also noted that the project was extremely ambitious: "Yes! But the Earth is very large, and life is very short! In order to leave a completed work behind, one would need to live to be at least 100 years old!"
Hetzel influenced many of Verne's novels directly, especially in the first few years of their collaboration, for Verne was initially so happy to find a publisher that he agreed to almost all of the changes Hetzel suggested. For example, when Hetzel disapproved of the original climax of Captain Hatteras, including the death of the title character, Verne wrote an entirely new conclusion in which Hatteras survived. Hetzel also rejected Verne's next submission, Paris in the Twentieth Century, believing its pessimistic view of the future and its condemnation of technological progress were too subversive for a family magazine. (The manuscript, believed lost for some time after Verne's death, was finally published in 1994.)
The relationship between publisher and writer changed significantly around 1869 when Verne and Hetzel were brought into conflict over the manuscript for Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas. Verne had initially conceived of the submariner Captain Nemo as a Polish scientist whose acts of vengeance were directed against the Russians who had killed his family during the January Uprising. Hetzel, not wanting to alienate the lucrative Russian market for Verne's books, demanded that Nemo be made an enemy of the slave trade, a situation that would make him an unambiguous hero. Verne, after fighting vehemently against the change, finally invented a compromise in which Nemo's past is left mysterious. After this disagreement, Verne became notably cooler in his dealings with Hetzel, taking suggestions into consideration but often rejecting them outright.
From that point, Verne published two or more volumes a year. The most successful of these are: Voyage au centre de la Terre (Journey to the Center of the Earth, 1864); De la Terre à la Lune (From the Earth to the Moon, 1865); Vingt mille lieues sous les mers (Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas, 1869); and Le tour du monde en quatre-vingts jours (Around the World in Eighty Days), which first appeared in Le Temps in 1872. Verne could now live on his writings, but most of his wealth came from the stage adaptations of Le tour du monde en quatre-vingts jours (1874) and Michel Strogoff (1876), which he wrote with Adolphe d'Ennery.
In 1867, Verne bought a small boat, the Saint-Michel, which he successively replaced with the Saint-Michel II and the Saint-Michel III as his financial situation improved. On board the Saint-Michel III, he sailed around Europe. After his first novel, most of his stories were first serialised in the Magazine d'Éducation et de Récréation, a Hetzel biweekly publication, before being published in book form. His brother Paul contributed to 40th French climbing of the Mont-Blanc and a collection of short stories – Doctor Ox – in 1874. Verne became wealthy and famous.
Meanwhile, Michel Verne married an actress against his father's wishes, had two children by an underage mistress and buried himself in debts. The relationship between father and son improved as Michel grew older.
THE
FATHER OF SCIENCE FICTION
Jules Verne
hit his stride as a writer after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel, who nurtured many of the works that would comprise the author's Voyages
Extraordinaires.
In all, Verne authored more than 60 books (most notably the 54 novels comprising the Voyages
Extraordinaires), as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including the
submarine, space travel, terrestrial flight and
deep-sea
exploration.

CLASSIC
WORKS - Jules Verne is best known for 20,000 leagues Under the Sea and
Around the World in Eighty Days, both of which became Hollywood
classics. Jules Verne was and still remains one of the best-renowned science fiction authors. His books were decades and even centuries ahead of their time, and while the initial reception to some of his books may have been muted they have nevertheless continued to amaze many as well as influence scientific discourse and debates. He remains unparalleled when it comes to science fiction and here are some of his top books.
Jules
Verne was the author of many adventure stories:
1
Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea
2 Around the World in Eighty Days
3 Journey to the Center of the Earth
4 The Mysterious Island (Extraordinary Voyages #12)
5 From the Earth to the Moon
6 Michael Strogoff (Extraordinary Voyages, #14)
7 In Search of the
Castaways; or the Children of Captain Grant (Extraordinary Voyages, #5)
8 Five Weeks in a Balloon
9
Round the Moon (Extraordinary Voyages, #7)
10 Adrift in the
Pacific: Two Years Holiday (Extraordinary Voyages, #32)
11 The Master of the World (Extraordinary Voyages, #53)
12 The Adventures of Captain Hatteras
13 Les Tribulations d'un Chinois en Chine;
The Tribulations of a Chinese in China (Extraordinary Voyages, #19)
14 The Lighthouse at the End of the World
15 Mathias Sandorf (Extraordinary Voyages, #27)
16 Off On A Comet (Extraordinary Voyages, #15)
17 Los quinientos millones de la Begún (The five hundred million of the
Begún)
18 Facing the Flag (Extraordinary Voyages, #42)
19 Un capitán de quince años (A fifteen year old captain)
20 El Testamento de un excentrico (The Testament of an eccentric)
Many
people have used the eighty day target set by Jules Verne as the
goalposts for their technology projects having been inspired by the
famous French author. We are likewise enthused.
|