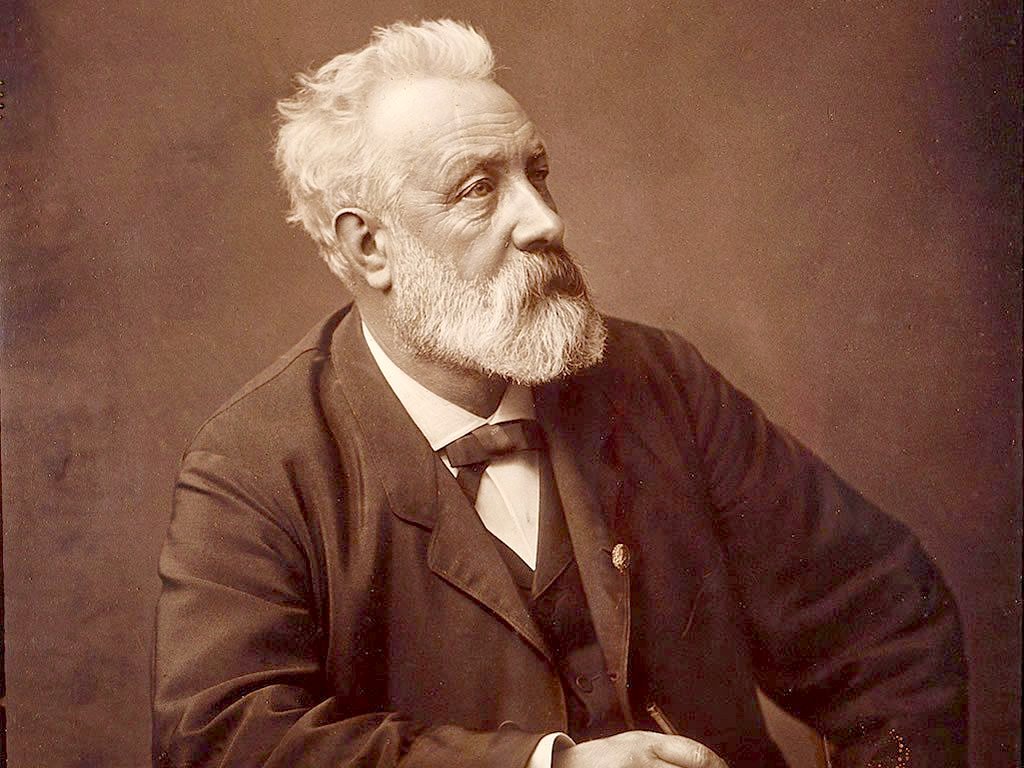|
What
a wonderful imagination the French writer had. He was also a practical
mariner, gaining much of his material from his travels, just like Herman
Melville, for his Moby
Dick. Jules Verne is best known for '20,000
Leagues Under the Sea' and Around
The World In Eighty Days. But he also authored a number of other
popular novels, that made it onto the big screen, such as 'The
Mysterious Island,' and 'Journey To The Centre Of The World.'
EARLY
LIFE
Jules
Verne was born on 8 February 1828, on Île Feydeau, a small artificial island on the Loire River within the town of Nantes, in No. 4 Rue Olivier-de-Clisson, the house of his maternal grandmother Dame Sophie Marie Adélaïde Julienne Allotte de La Fuÿe (born Guillochet de La Perrière). His parents were Pierre Verne, an attorney originally from Provins, and Sophie Allotte de La Fuÿe, a Nantes woman from a local family of navigators and shipowners, of distant Scottish descent. In 1829, the Verne family moved some hundred metres away to No. 2 Quai Jean-Bart, where Verne's brother Paul was born the same year. Three sisters, Anne "Anna" (1836), Mathilde (1839), and Marie (1842) would follow.
In 1834, at the age of six, Verne was sent to boarding school at 5 Place du Bouffay in Nantes. The teacher, Madame Sambin, was the widow of a naval captain who had disappeared some 30 years before.[10] Madame Sambin often told the students that her husband was a shipwrecked castaway and that he would eventually return like Robinson Crusoe from his desert island
paradise. The theme of the robinsonade would stay with Verne throughout his life and appear in many of his novels, including The Mysterious Island (1874), Second Fatherland (1900), and The School for Robinsons (1882).
In 1836, Verne went on to École Saint‑Stanislas, a Catholic school suiting the pious religious tastes of his father. Verne quickly distinguished himself in mémoire (recitation from memory), geography, Greek, Latin, and singing. In the same year, 1836, Pierre Verne bought a vacation house at 29 Rue des Réformés in the village of Chantenay (now part of Nantes) on the Loire River. In his brief memoir Souvenirs d'enfance et de jeunesse (Memories of Childhood and Youth, 1890), Verne recalled a deep fascination with the river and with the many merchant vessels navigating it. He also took vacations at Brains, in the house of his uncle Prudent Allotte, a retired shipowner, who had gone around the world and served as mayor of Brains from 1828 to 1837. Verne took joy in playing interminable rounds of the Game of the Goose with his uncle, and both the game and his uncle's name would be memorialized in two late novels (The Will of an Eccentric (1900) and Robur the Conqueror (1886), respectively).
Legend has it that in 1839, at the age of 11, Verne secretly procured a spot as cabin boy on the three-mast ship Coralie with the intention of traveling to the Indies and bringing back a
coral necklace for his cousin Caroline. The evening the ship set out for the Indies, it stopped first at Paimboeuf where Pierre Verne arrived just in time to catch his son and make him promise to travel "only in his imagination". It is now known that the legend is an exaggerated tale invented by Verne's first biographer, his niece Marguerite Allotte de la Füye, though it may have been inspired by a real incident.
In 1840, the Vernes moved again to a large apartment at No. 6 Rue Jean-Jacques-Rousseau, where the family's youngest child, Marie, was born in 1842. In the same year Verne entered another religious school, the Petit Séminaire de Saint-Donatien, as a lay student. His unfinished novel Un prêtre en 1839 (A Priest in 1839), written in his teens and the earliest of his prose works to survive, describes the seminary in disparaging terms. From 1844 to 1846, Verne and his brother were enrolled in the Lycée Royal (now the Lycée Georges-Clemenceau) in Nantes. After finishing classes in rhetoric and philosophy, he took the baccalauréat at Rennes and received the grade "Good Enough" on 29 July 1846.
By 1847, when Verne was 19, he had taken seriously to writing long works in the style of Victor Hugo, beginning Un prêtre en 1839 and seeing two verse tragedies, Alexandre VI and La Conspiration des poudres (The Gunpowder Plot), to completion. However, his father took it for granted that Verne, being the firstborn son of the family, would not attempt to make money in literature but would instead inherit the family law practice.
In 1847, Verne's father sent him to Paris, primarily to begin his studies in law school, and secondarily (according to family legend) to distance him temporarily from Nantes. His cousin Caroline, with whom he was in love, was married on 27 April 1847, to Émile Dezaunay, a man of 40, with whom she would have five children.
After a short stay in Paris, where he passed first-year law exams, Verne returned to Nantes for his father's help in preparing for the second year. (Provincial law students were in that era required to go to Paris to take exams.) While in Nantes, he met Rose Herminie Arnaud Grossetière, a young woman one year his senior, and fell intensely in love with her. He wrote and dedicated some thirty poems to her, including La Fille de l'air (The Daughter of Air), which describes her as "blonde and enchanting / winged and transparent". His passion seems to have been reciprocated, at least for a short time, but Grossetière's parents frowned upon the idea of their daughter marrying a young student of uncertain future. They married her instead to Armand Terrien de la Haye, a rich landowner ten years her senior, on 19 July 1848.
The sudden marriage sent Verne into deep frustration. He wrote a hallucinatory letter to his mother, apparently composed in a state of half-drunkenness, in which under pretext of a dream he described his misery. This requited but aborted love affair seems to have permanently marked the author and his work, and his novels include a significant number of young women married against their will (Gérande in Master Zacharius (1854), Sava in Mathias Sandorf (1885), Ellen in A Floating City (1871), etc.), to such an extent that the scholar Christian Chelebourg attributed the recurring theme to a "Herminie complex". The incident also led Verne to bear a grudge against his birthplace and Nantes society, which he criticized in his poem La sixième ville de France (The Sixth City of France).
THE
FATHER OF SCIENCE FICTION
Jules Verne
hit his stride as a writer after meeting publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel, who nurtured many of the works that would comprise the author's Voyages
Extraordinaires.
In all, Verne authored more than 60 books (most notably the 54 novels comprising the Voyages
Extraordinaires), as well as dozens of plays, short stories and librettos. He conjured hundreds of memorable characters and imagined countless innovations years before their time, including the submarine, space travel, terrestrial flight and deep-sea exploration.

CLASSIC
WORKS - Jules Verne is best known for 20,000 leagues Under the Sea and
Around the World in Eighty Days, both of which became Hollywood
classics. Jules Verne was and still remains one of the best-renowned science fiction authors. His books were decades and even centuries ahead of their time, and while the initial reception to some of his books may have been muted they have nevertheless continued to amaze many as well as influence scientific discourse and debates. He remains unparalleled when it comes to science fiction and here are some of his top books.
Jules
Verne was the author of many adventure stories:
1
Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea
2 Around the World in Eighty Days
3 Journey to the Center of the Earth
4 The Mysterious Island (Extraordinary Voyages #12)
5 From the Earth to the Moon
6 Michael Strogoff (Extraordinary Voyages, #14)
7 In Search of the
Castaways; or the Children of Captain Grant (Extraordinary Voyages, #5)
8 Five Weeks in a Balloon
9
Round the Moon (Extraordinary Voyages, #7)
10 Adrift in the
Pacific: Two Years Holiday (Extraordinary Voyages, #32)
11 The Master of the World (Extraordinary Voyages, #53)
12 The Adventures of Captain Hatteras
13 Les Tribulations d'un Chinois en Chine;
The Tribulations of a Chinese in China (Extraordinary Voyages, #19)
14 The Lighthouse at the End of the World
15 Mathias Sandorf (Extraordinary Voyages, #27)
16 Off On A Comet (Extraordinary Voyages, #15)
17 Los quinientos millones de la Begún (The five hundred million of the
Begún)
18 Facing the Flag (Extraordinary Voyages, #42)
19 Un capitán de quince años (A fifteen year old captain)
20 El Testamento de un excentrico (The Testament of an eccentric)
Many
people have used the eighty day target set by Jules Verne as the
goalposts for their technology projects having been inspired by the
famous French author. We are likewise enthused.
|