|
The
legend of Atlantis was created by Plato some 2,300 years ago. Plato
claimed that this utopian civilization, that allegedly existed 9,000
years before even his time, was punished by the gods for becoming
selfish, greedy, and amoral and thus sunk into the seas. Which sea or
ocean is not known for sure, but it most likely be in the Mediterranean
or Atlantic
- fictionally.
It
is possible that the legend was inspired by Plato's knowledge of other
subsea ruins, as fishermen and pearl divers of the day returned from Inner
Space forays.
The ocean is home to many myths, legends and mysteries. While scientists have succeeded in explaining many of these mysteries, there are quite a few still remaining as unexplained.
Lost cities, hidden treasures, mystic ships are all part of the alluring marine world. Of all these, the lost city of Atlantis tops the list.
All available evidence indicates that the philosopher Plato, sometime around 360 BCE, invented the island nation in order to illustrate a point about the dangers of aggressive imperialism. In Plato’s telling, Atlantis was no utopia. Rather, it was a foil for an idealized version of Athens from long before Plato’s time.
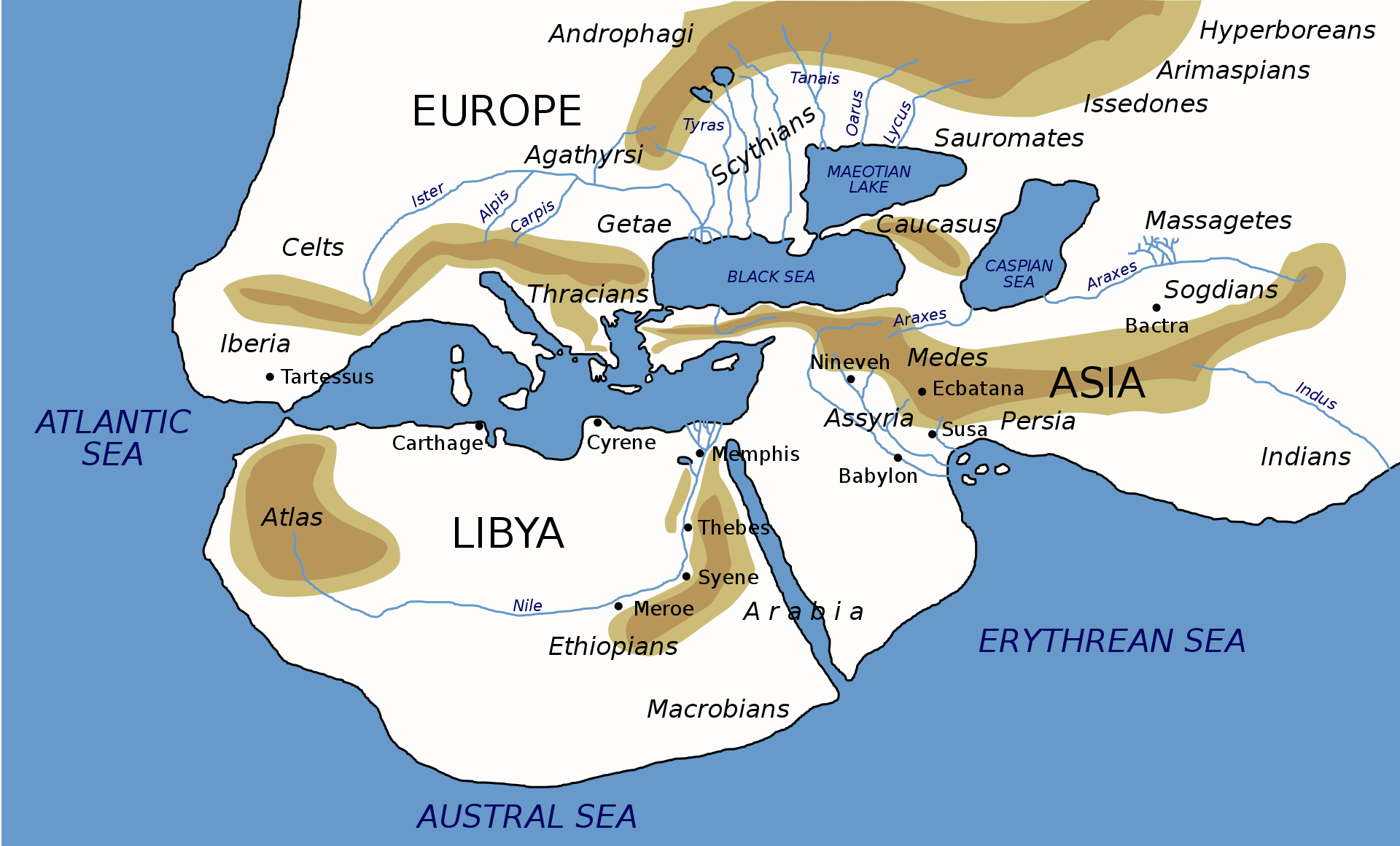
In Plato’s texts, Atlantis was “larger than Libya and Asia combined,” (which, in Plato’s time, would have referred to modern-day northern Africa and over half of Turkey). It was situated in the Atlantic Ocean, somewhere outward from the Strait of Gibraltar.
For a long time, Azores was believed to be the site of the city of Atlantis. However, the new researches have revealed a new site and the scientists are sure that Atlantis can be found in Cadiz, somewhere between the Spain and Morocco waters.

In 1882, the former U.S. Congressman, Ignatius Donnelly, published Atlantis: The Antediluvian World. The book laid out 13 hypotheses, centered on the idea that Atlantis had truly existed, and indeed represented a place “where early mankind dwelt for ages in peace and happiness.” According to Donnelly, Atlantis was the original source of many ancient civilizations around the world. If one followed the clues in Plato’s writing, Donnelly believed, Atlantis could be found.
In the years after Columbus brought news of the New World back to Europe, many claimed that America was the fabled Atlantis. But the search really gained steam in the 20th and 21st centuries. Some searchers have pointed to a volcanic eruption that destroyed parts of the island of Santorini around 1600 BCE, wiping out Minoan settlements. And in 2018, a team announced, to much fanfare, that they had found “CONCRETE proof that Atlantis existed.” Key evidence included a series of circles in a national park in Spain. They turned out to be experimental ponds created in 2004 and 2005 for a study involving zooplankton.
Legend says that the Atlantis city was built by Poseidon- the God of Sea, of storms and earthquakes- when he fell in love with a mortal woman Cleito. He made this city on top of a hill, on an isolated island in the sea, to protect her and named it Atlantis.
According to the story, Poseidon walked through the world in an effort to find the biggest island until he reached the biggest of them all Atlantis and found it to be inhabited by people who were more beautiful and intelligent than the rest of the world.
It was then he fell in love with Cleito when he finds her on the island.
POSSIBLE LOCATIONS
There have been dozens of locations proposed for Atlantis, to the point where the name has become a generic concept, divorced from the specifics of Plato's account. This is reflected in the fact that many proposed sites are not within the Atlantic at all.
MEDITERRANEAN SEA
Most of the historically proposed locations are in or near the Mediterranean Sea: islands such as Sardinia, Crete, Santorini (Thera), Sicily, Cyprus, and Malta; land-based cities or states such as Troy, Tartessos, and Tantalis (in the province of Manisa, Turkey); Israel-Sinai or Canaan; and northwestern Africa.
The Thera eruption, dated to the seventeenth or sixteenth century BC, caused a large tsunami that some experts hypothesize devastated the Minoan civilization on the nearby island of Crete, further leading some to believe that this may have been the catastrophe that inspired the story. In the area of the Black Sea the following locations have been proposed: Bosporus and Ancomah (a legendary place near Trabzon).
Others have noted that, before the sixth century BC, the mountains on either side of the Gulf of Laconia were called the "Pillars of Hercules", and they could be the geographical location being described in ancient reports upon which Plato was basing his story. The mountains stood at either side of the southernmost gulf in Greece, the largest in the Peloponnese, and that gulf opens onto the Mediterranean Sea. If from the beginning of discussions, misinterpretation of Gibraltar as the location rather than being at the Gulf of Laconia, would lend itself to many erroneous concepts regarding the location of Atlantis. Plato may have not been aware of the difference. The Laconian pillars open to the south toward Crete and beyond which is Egypt. The Thera eruption and the Late Bronze Age collapse affected that area and might have been the devastation to which the sources used by Plato referred. Significant events such as these would have been likely material for tales passed from one generation to another for almost a thousand years.
JUST
A MYTH: Few, if any, scientists think Atlantis actually existed. Ocean explorer Robert Ballard, the National Geographic explorer-in-residence who discovered the wreck of the Titanic in 1985, notes that "no Nobel laureates" have said that what Plato wrote about Atlantis is true.
Still, Ballard says, the legend of Atlantis is a "logical" one since cataclysmic floods and volcanic explosions have happened throughout history, including one event that had some similarities to the story of the destruction of Atlantis. About 3,600 years ago, a massive volcanic eruption devastated the island of Santorini in the Aegean Sea near Greece. At the time, a highly advanced society of Minoans lived on Santorini. The Minoan civilization disappeared suddenly at about the same time as the volcanic eruption.
ATLANTIC OCEAN
The location of Atlantis in the Atlantic Ocean has a certain appeal given the closely related names. Popular culture often places Atlantis there, perpetuating the original Platonic setting as they understand it. The Canary Islands and Madeira Islands have been identified as a possible location, west of the Straits of Gibraltar, but in relative proximity to the Mediterranean Sea. Detailed studies of their geomorphology and geology have demonstrated, however, that they have been steadily uplifted, without any significant periods of subsidence, over the last four million years, by geologic processes such as erosional unloading, gravitational unloading, lithospheric flexure induced by adjacent islands, and volcanic underplating.
Various islands or island groups in the Atlantic were also identified as possible locations, notably the Azores. Similarly, cores of sediment covering the ocean bottom surrounding the Azores and other evidence demonstrate that it has been an undersea plateau for millions of years. The area is known for its volcanism however, which is associated with rifting along the Azores Triple Junction. The spread of the crust along the existing faults and fractures has produced many volcanic and seismic events. The area is supported by a buoyant upwelling in the deeper mantle, which some associate with an Azores hotspot. Most of the volcanic activity has occurred primarily along the Terceira Rift. From the beginning of the islands' settlement, around the 15th century, there have been about 30 volcanic eruptions (terrestrial and submarine) as well as numerous, powerful earthquakes. The island of São Miguel in the Azores is the site of the Sete Cidades volcano and caldera, which are the byproducts of historical volcanic activity in the Azores.
The submerged island of Spartel near the Strait of Gibraltar has also been suggested.
IRELAND
In 2004, Swedish physiographist Ulf Erlingsson proposed that the legend of Atlantis was based on Stone Age Ireland. He later stated that he does not believe that Atlantis ever existed but maintained that his hypothesis that its description matches Ireland's geography has a 99.8% probability. The director of the National Museum of Ireland commented that there was no archaeology supporting this.
IN EUROPE
Several hypotheses place the sunken island in northern Europe, including Doggerland in the North Sea, and Sweden (by Olof Rudbeck in Atland, 1672–1702). Doggerland, as well as Viking Bergen Island, is thought to have been flooded by a megatsunami following the Storegga slide of c. 6100 BC. Some have proposed the Celtic Shelf as a possible location, and that there is a link to Ireland.
In 2011, a team, working on a documentary for the National Geographic Channel, led by Professor Richard Freund from the University of Hartford, claimed to have found possible evidence of Atlantis in southwestern Andalusia. The team identified its possible location within the marshlands of the Doñana National Park, in the area that once was the Lacus Ligustinus, between the Huelva, Cádiz, and Seville provinces, and they speculated that Atlantis had been destroyed by a tsunami, extrapolating results from a previous study by Spanish researchers, published four years earlier.
Spanish scientists have dismissed Freund's speculations, claiming that he sensationalised their work. The anthropologist Juan Villarías-Robles, who works with the Spanish National Research Council, said, "Richard Freund was a newcomer to our project and appeared to be involved in his own very controversial issue concerning King Solomon's search for ivory and gold in Tartessos, the well documented settlement in the Doñana area established in the first millennium BC", and described Freund's claims as "fanciful".
A similar theory had previously been put forward by a German researcher, Rainer W. Kühne, that is based only on satellite imagery and places Atlantis in the Marismas de Hinojos, north of the city of Cádiz. Before that, the historian Adolf Schulten had stated in the 1920s that Plato had used Tartessos as the basis for his Atlantis myth.
OTHER LOCATIONS
Several writers, such as Flavio Barbiero as early as 1974, have speculated that Antarctica is the site of Atlantis. A number of claims involve the Caribbean, such as an alleged underwater formation off the Guanahacabibes peninsula in Cuba. The adjacent Bahamas or the folkloric Bermuda Triangle have been proposed as well. Areas in the Pacific and Indian Oceans have also been proposed, including Indonesia (i.e. Sundaland). The stories of a lost continent off the coast of India, named "Kumari Kandam", have inspired some to draw parallels to Atlantis.
Ocean
literacy
could be taught in schools, as part of an educational
curriculum.
What
lost treasures might we discover as the mysteries of the deep unfold,
armed with new underwater technology and a army of freshly educated
researchers with an interest in the deep.
ATLANTIS
- MEDITERRANEAN SEA
ATLIT-YAM - ISRAEL
BAIA - ITALY
DWARKA - INDIA
PAVLOPETRI - GREECE
PHANAGORIA - BLACK SEA
PORT ROYAL - JAMAICA
RUNGHOLT
- DENMARK
THONIS-HERACLEION AND ALEXANDRIA - EGYPT
YONAGUNI JIMA - JAPAN
REFERENCE
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/history/article/atlantis
|



